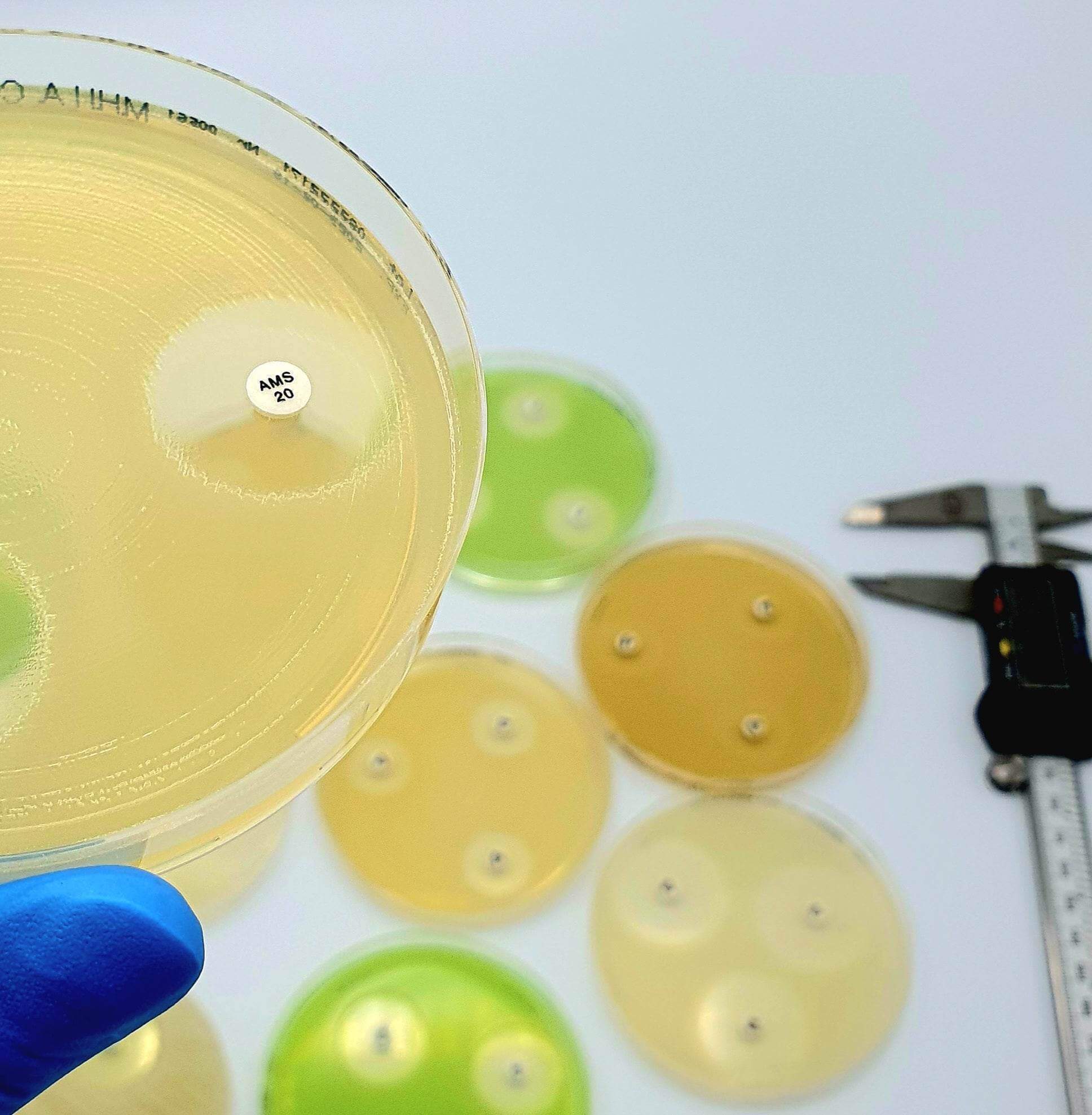
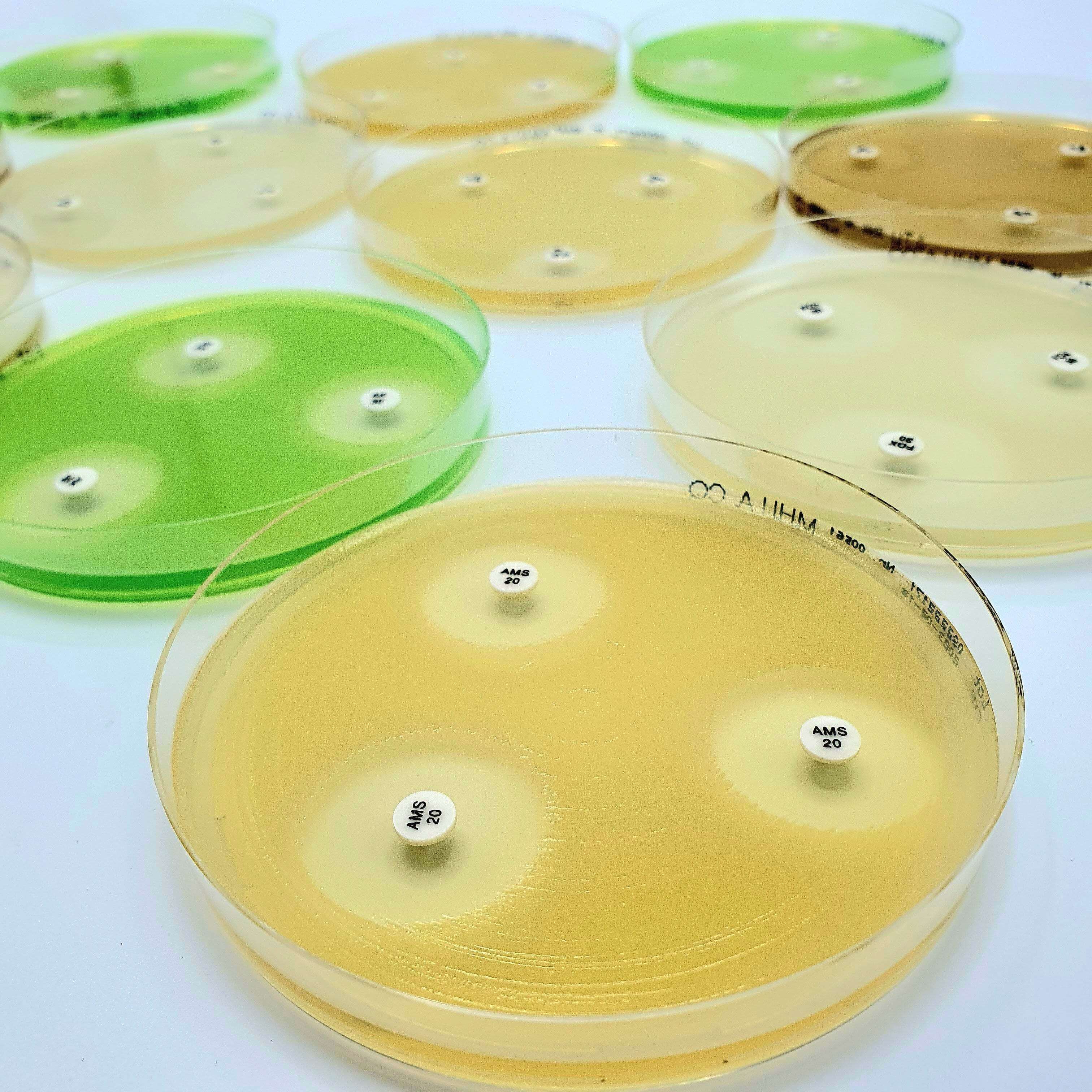
Description
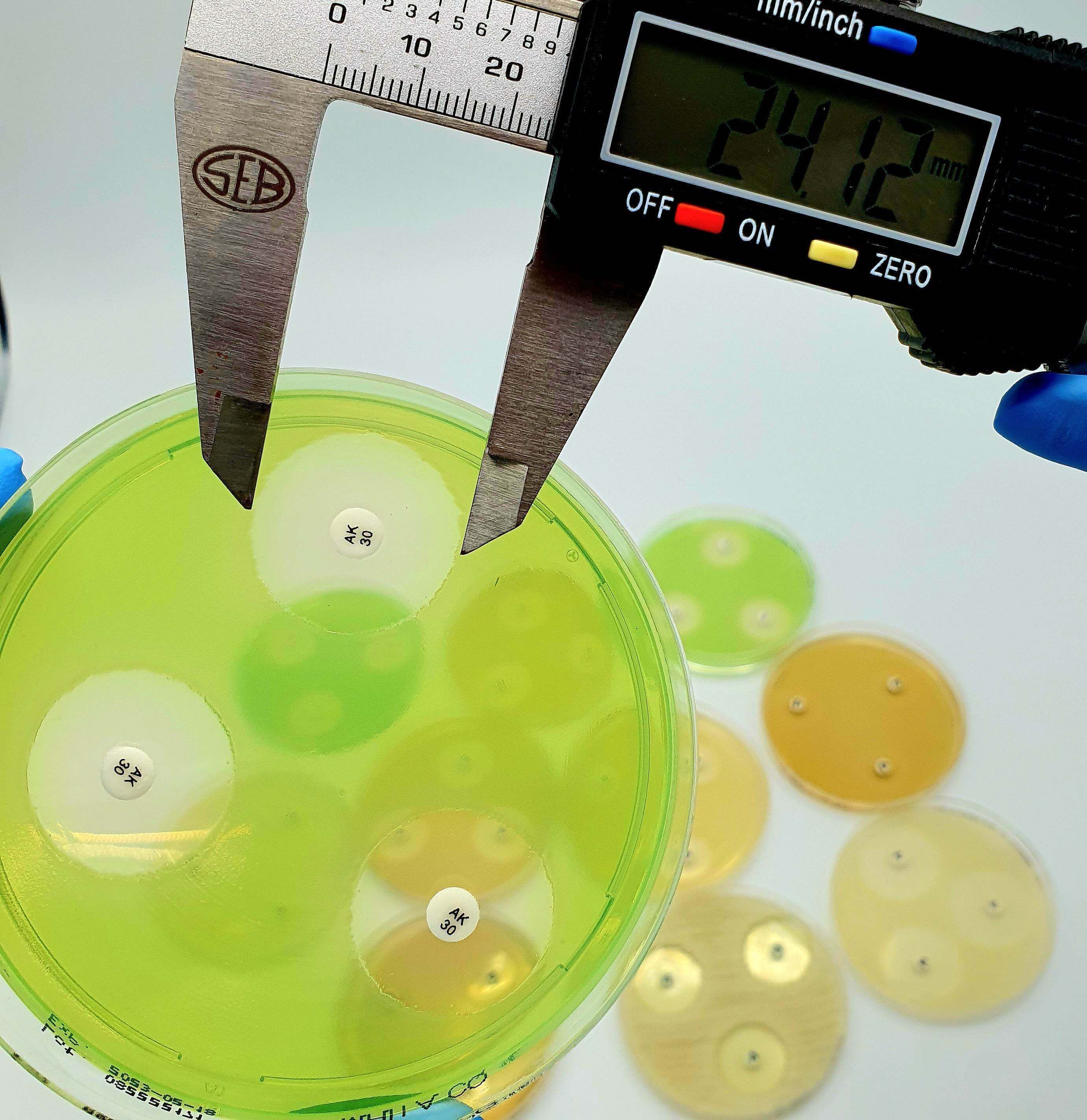
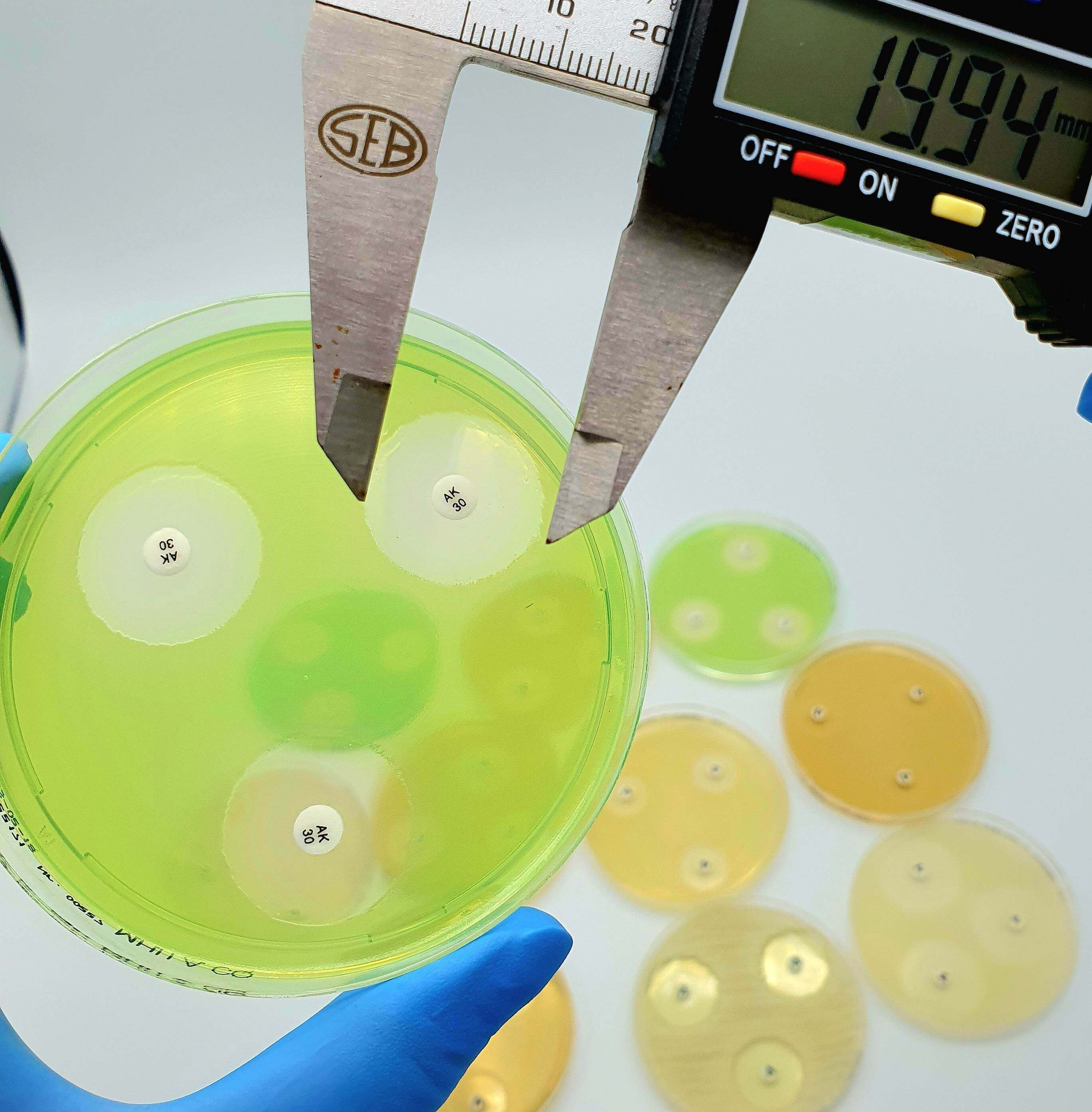
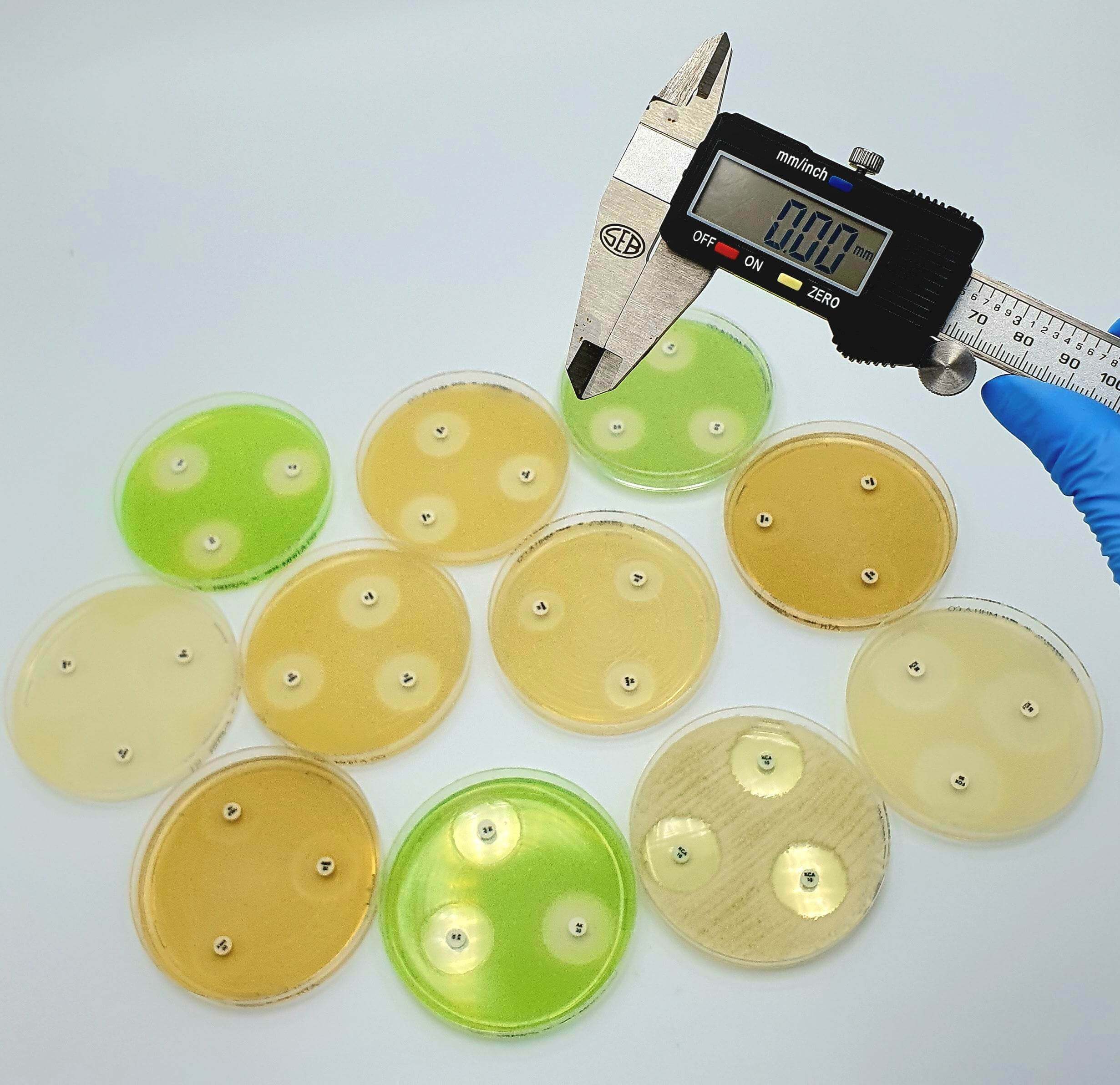
Disc tests for confirmation of ESBLs in organisms with chromosomally encoded inducible AmpC.
Extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) are enzymes hydrolyzing most penicillins and cephalosporins, including oxyiminoβ-lactam compunds but not cephamycins and carbapenems. Most ESBLs belong to the Ambler class A of β-lactamases and
are inhibited by β-lactamases inhibitors: clavulanic acid, sulbatam and tazobactam. ESBL production has been observed mostly in Enterobacteriaceae, particularly Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pnuemoniae, but all other clinically-relevant
Enterobacteriaceae species are also common ESBL-producers. In many areas, ESBL detection and characterization is recommended or mandatory for infection control purpose.
Payment & Security
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.